Source(google.com.pk)
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi (the brand name for products using IEEE 802.11 standards) have some similar applications: setting up networks, printing, or transferring files. Wi-Fi is intended as a replacement for cabling for general local area network access in work areas. This category of applications is sometimes called wireless local area networks (WLAN). Bluetooth was intended for portable equipment and its applications. The category of applications is outlined as the wireless personal area network (WPAN). Bluetooth is a replacement for cabling in a variety of personally carried applications in any setting and also works for fixed location applications such as smart energy functionality in the home (thermostats, etc.).
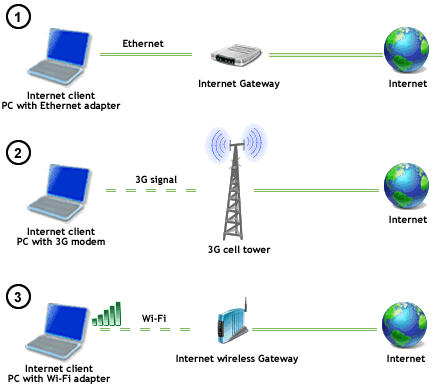
Wi-Fi is a wireless version of a common wired Ethernet network, and requires configuration to set up shared resources, transmit files, and to set up audio links (for example, headsets and hands-free devices). Wi-Fi uses the same radio frequencies as Bluetooth, but with higher power, resulting in higher bit rates and better range from the base station. The nearest equivalents in Bluetooth are the DUN profile, which allows devices to act as modem interfaces, and the PAN profile, which allows for ad-hoc networking.
Bluetooth exists in many products, such as telephones, tablets, media players, Lego Mindstorms NXT, PlayStation 3, PS Vita, the Nintendo Wii, and some high definition headsets, modems, and watches. The technology is useful when transferring information between two or more devices that are near each other in low-bandwidth situations. Bluetooth is commonly used to transfer sound data with telephones (i.e., with a Bluetooth headset) or byte data with hand-held computers (transferring files).
Bluetooth protocols simplify the discovery and setup of services between devices. Bluetooth devices can advertise all of the services they provide. This makes using services easier because more of the security, network address and permission configuration can be automated than with many other network types.
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi (the brand name for products using IEEE 802.11 standards) have some similar applications: setting up networks, printing, or transferring files. Wi-Fi is intended as a replacement for cabling for general local area network access in work areas. This category of applications is sometimes called wireless local area networks (WLAN). Bluetooth was intended for portable equipment and its applications. The category of applications is outlined as the wireless personal area network (WPAN). Bluetooth is a replacement for cabling in a variety of personally carried applications in any setting and also works for fixed location applications such as smart energy functionality in the home (thermostats, etc.).
Wi-Fi is a wireless version of a common wired Ethernet network, and requires configuration to set up shared resources, transmit files, and to set up audio links (for example, headsets and hands-free devices). Wi-Fi uses the same radio frequencies as Bluetooth, but with higher power, resulting in higher bit rates and better range from the base station. The nearest equivalents in Bluetooth are the DUN profile, which allows devices to act as modem interfaces, and the PAN profile, which allows for ad-hoc networking.
Bluetooth exists in many products, such as telephones, tablets, media players, Lego Mindstorms NXT, PlayStation 3, PS Vita, the Nintendo Wii, and some high definition headsets, modems, and watches. The technology is useful when transferring information between two or more devices that are near each other in low-bandwidth situations. Bluetooth is commonly used to transfer sound data with telephones (i.e., with a Bluetooth headset) or byte data with hand-held computers (transferring files).
Bluetooth protocols simplify the discovery and setup of services between devices. Bluetooth devices can advertise all of the services they provide. This makes using services easier because more of the security, network address and permission configuration can be automated than with many other network types.
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
 Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi
Bluetooth vs Wi-Fi









No comments:
Post a Comment